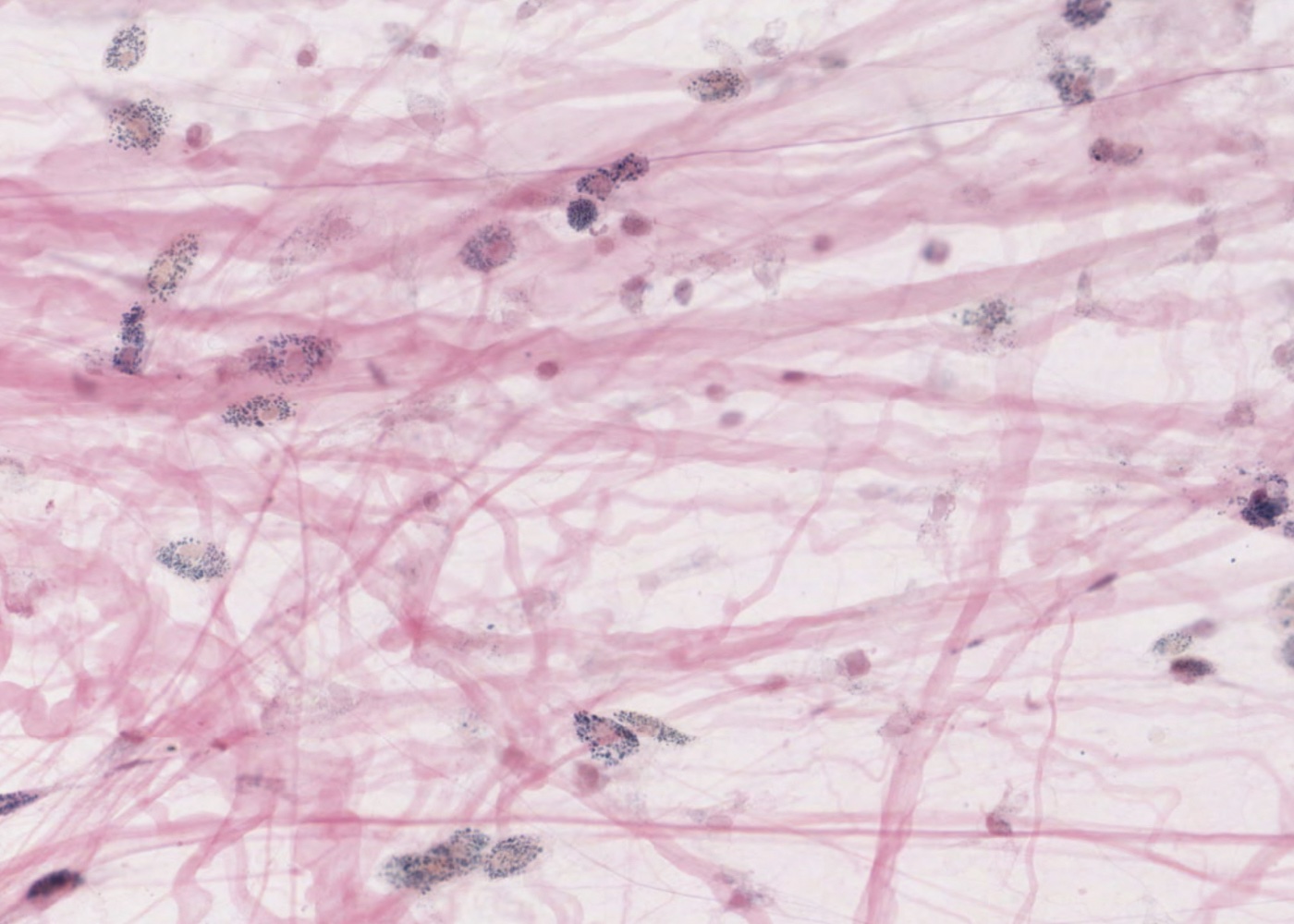
Connective tissue is widespread throughout the body and consists of cells, fibers and matrix. The types of connective tissues depends on which of these three components dominate (functionally).
Learning outcomes
You should be able to identify the following in tissue sections and appreciate their functional significances:
- Loose connective tissue.
- Collagen fibers/fibres.
- Dense, irregular connective tissue.
- Dense, regular connective tissue.
- Reticular connective tissue.
- Reticular fibers/fibres.
- Elastic fibers/fibres (when stained).
- Elastic lamina (when stained).
- Adipose tissue (yellow fat).
- Brown fat.
- Stroma.
- Fibroblasts.
- Macrophages when vitally stained.
- Mast cells.
- Adipocytes.