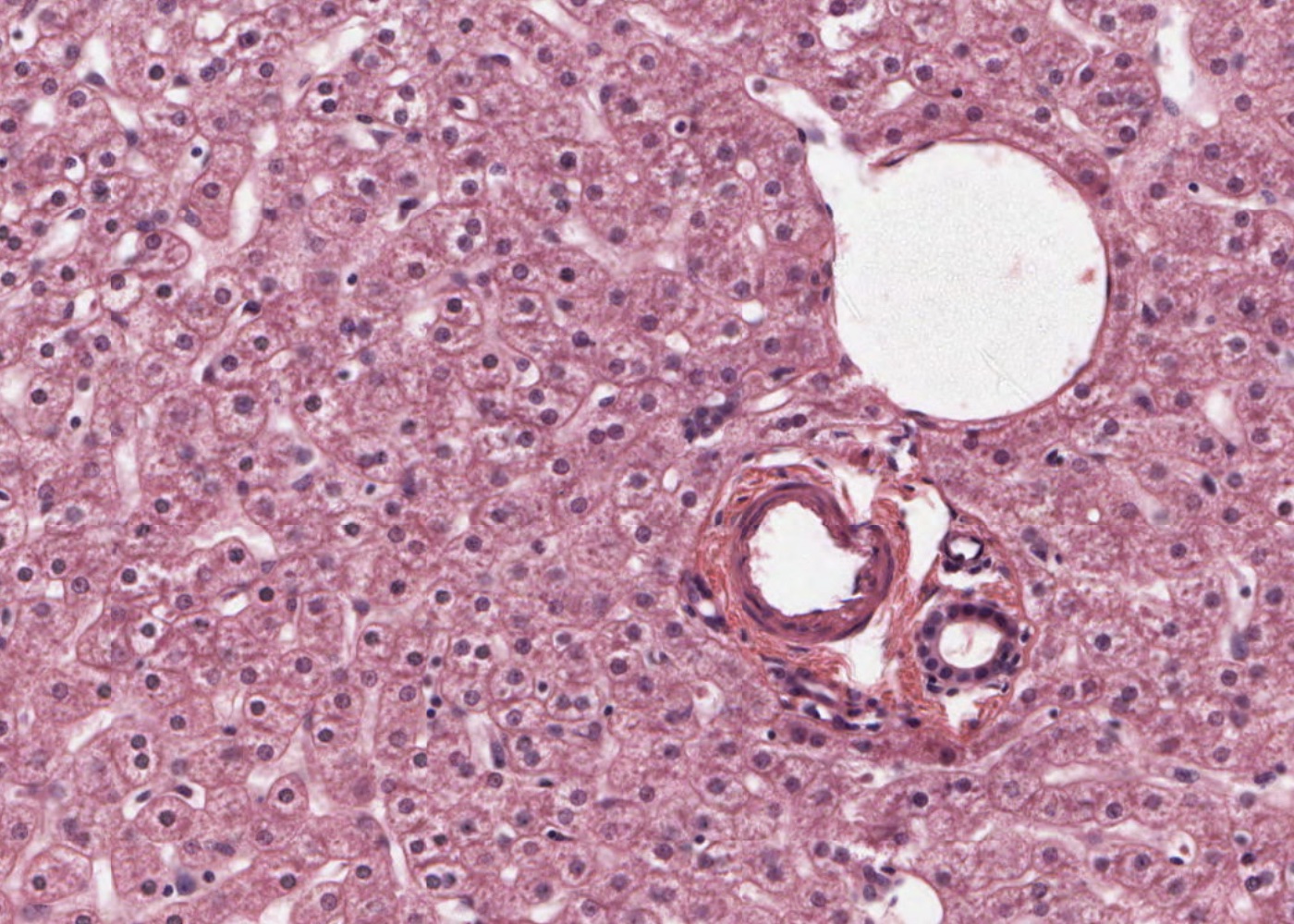
The liver is the largest glandular tissue in the human body and has many important functions including receiving, storing and distributing nutrients required by body cells; producing most of our plasma proteins; converting vitamins, storing iron and detoxifing toxins and drugs. The liver also produces bile and assumes an endocrine role.
The pancreas is both an exocrine and an endocrine gland. The histological features performing its endocrine role is described in the “Endocrine system“. In this module, the exocrine pancreas is described – that serous acinar component synthesizing and secreting digestive enzymes.
The gallbladder concentrates and stores bile.
Learning outcomes
After viewing the images and the histological sections available you should
- know main functions of the liver: can you name 6 functions or even more?
- Identify structures found in a portal area.
- know from which organs portal blood flow to the liver comes from?
- know the structure of a classic liver lobule.
- know what portion of the liver is the most active metabolically?
- describe the space of Disse?
- understand what forms the walls of a bile canaliculus?
- know histological characteristics of the mucosa of the gallbladder?
- know functions of the gallbladder.
- know the endocrine and exocrine cells of the pancreas, and their secretory products.
- know what regulates the secretion of these pancreatic cells?
- describe and identify components of the exocrine pancreas duct system.