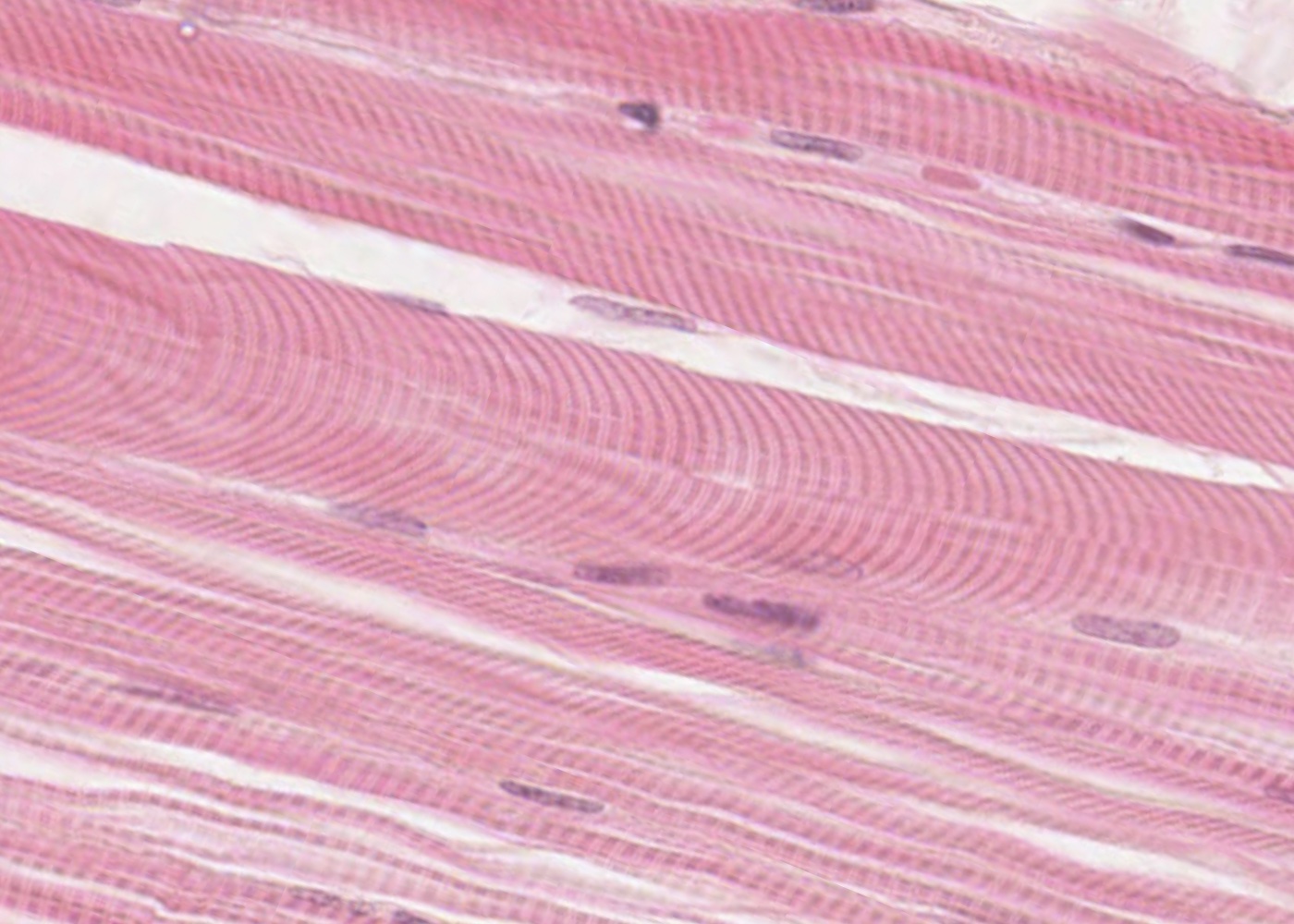
Muscle tissue is specialised for contraction and so effects movement of our body, the pumping action of the chambers of our heart and changes the size and shape of many internal organs.
Learning outcomes
After viewing the histological images and interactive text in this module you should
- recognize skeletal striated muscle, cardiac striated muscle and smooth muscle in longitudinal and transverse section.
- recognize the following structures associated with:
Skeletal striated muscle
skeletal muscle fiber
endomysium
perimysium
fascicle
myofibril
sarcomere
relaxed band pattern
contracted band pattern
A band, I band, Z line
muscle spindle
intrafusal fibers
extrafusal fibers
Cardiac striated muscle
branching fibers
myofibrils
cross bands
central nuclei
intercalated disks stained with PAS and stained with H&E
Smooth muscle
nucleus (contracted and resting)
cytoplasm